-
- About Odus
- Vision
- Overseas cooperation
- Quality control
- Location
-
- Contact us
- Contact us
-
- Odus News
- Odus News
- Newsletter
 What is Bio-Stimulant?
What is Bio-Stimulant?Plant biostimulants contain substance(s) and/or micro-organisms whose function when applied to plants or the rhizosphere is to stimulate natural processes to enhance/benefit nutrient uptake, nutrient efficiency, tolerance to abiotic stress, and crop quality.
- EBIC-European Bio-Stimulant Industry Council -
 Odus Product
Odus ProductOdus is the first company in Korea to define and commercialise biostimulant products with its own formulation derived from exact principle and function
 Differences Bio-Stimulant and Fertiliser
Differences Bio-Stimulant and Fertiliser| Fertiliser | Bio-Stimulant | |
|---|---|---|
| Usage | Much(100-300kg N/ha) | little(0.5-1kg N/ha) |
| Process | Soil fertilization and foliar application | Foliar spray, soil drench and soil fertilization |
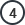 Advantages of Bio-Stimulant comparing Fertiliser
Advantages of Bio-Stimulant comparing Fertiliser| Advantages | Effects | Mechanisms |
|---|---|---|
| Growth and Yield |
1. Effectively used for the growth of stems and roots 2. Promote flowering and flower bud differentiation 3. Promote fruiting and yield increase |
1. Facilitating movement of nutrients 2. Promote photosynthesis 3. Promote flowering and flower bud differentiation 4. Facilitate the movement of sugars and accumulation |
| Quality |
1. Crop Quality Improvement 2. Reduce the accumulation of nitrogen, reduction of soil degradation |
1. Protein synthesis, photosynthesis, the assimilation and promote 2. Flavor, texture improved |
| The use of nutritional substances |
1. Land utilization improved 2. Improve transport of nutrients |
1. The use of nutritional substances in accordance with the chelating effect |
| Stress |
1. Magnetic resistance Crop Promotion 2. Promote resistance to temperatures, salt, drought, cold, etc. 3. Promotion of improved root development and nutrient |
1. Promotion of improved root development and nutrient 2. The stabilization of cell membranes and osmotic substance 3. Promoting enzyme system for preventing stress |
| Soil fertility | 1. Promote the beneficial microorganisms → Promotion of soil fertility |
1. Promote soil microbial activity within the (Inhibit harmful bacteria density) 2. the use of amino acid as a feed of the microorganisms, |
 Bio-Stimulant as Bio-Fertilizer and Bio-Pesticide
Bio-Stimulant as Bio-Fertilizer and Bio-Pesticide